Chikungunya Virus
Chikungunya virus (pronounced: CHIK-en-GUUN-ye) or CHIKV, is an arbovirus carried by infected mosquitoes. The name is an African word meaning “that which bends up,” referring to the joint pains of those infected. Though CHIKV does not often result in death, the symptoms can be disabling, and some may develop severe complications. In severe cases it can be painful with symptoms lasting weeks or even years. Complications are rare, but more common in infants (<1 year), elderly (>65 years) and people with other chronic conditions such as weak immune systems, diabetes, hypertension, etc.
Background
Outbreaks have occurred in Africa, Asia, Europe and the Indian and Pacific Ocean regions. In late 2013, Chikungunya virus was found for the first time in the Caribbean islands. An average of 28 CHIKV infections has been reported annually since 2006 in the United States among travelers to affected areas. The number of cases continues to rise in 2014. Chikungunya virus is not currently found in the United States. There is a risk the virus will be imported to new areas by infected travelers.
Symptoms
Sudden onset of high fever (>102ºF), muscle aches, severe joint pain mainly in the arms, back, and legs, headache, and rash. Symptoms appear on average three to seven days after being bitten by an infected mosquito. Most patients feel better after a few days or weeks. Some people may develop long-term joint pain. If you have symptoms, record your symptoms and see a doctor. Your doctor may order blood tests which may include tests for both chikungunya (CHIKV) and dengue fever (DF), especially if you recently traveled to the Caribbean or South America. DF is another mosquito-borne illness similar to chikungunya. If you are sick with CHIKV, avoiding gettoing bit by mosquito will help protect others from CHIKV.
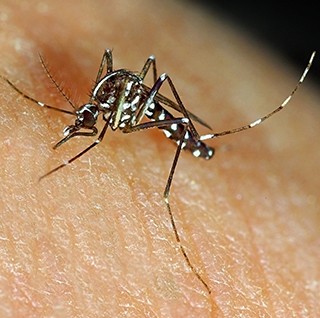
Transmission
CHIKV is most often spread to people by Aedes aegypti and Aedes albopictus mosquitoes. These are the same mosquitoes that transmit the virus that causes Dengue fever. They bite mostly during the daytime. If a person is infected and bitten by a mosquito, that mosquito may later spread the virus by biting another person. The female mosquito of this type lives three to four weeks and can bite every three to four days.
Treatment
There is no cure for this virus. However, using medicines (other than aspirin) to lower fever and joint pain may help.
Prevention
- Wear long-sleeved shirts and long pants.
- Use mosquito repellent on exposed skin.
- Ensure window/door screens are intact.
- Prevent standing water to prevent mosquitoes.
- Wear permethrin-treated clothing to repel and kill mosquitoes.
- Use air conditioning when available to make households less accessible to mosquitoes.

 TARRANT COUNTY, TX
TARRANT COUNTY, TX

 Epidemiology
Epidemiology